Understanding METAR Reports: A Crucial Tool for Weather Information in Aviation
METAR (Meteorological Aerodrome Report) is an essential weather observation report used in aviation to provide accurate and timely information about current weather conditions at airports and aerodromes. Understanding METAR reports is crucial for pilots, air traffic controllers, and drone operators to ensure safe and efficient operations.
-

Abhijit Shingate
CEO & Founder
Introduction:
METAR (Meteorological Aerodrome Report) is an essential weather observation report used in aviation to provide accurate and timely information about current weather conditions at airports and aerodromes. Understanding METAR reports is crucial for pilots, air traffic controllers, and drone operators to ensure safe and efficient operations. In this article, we will delve into the need for METAR reports, their format, the importance of being able to read them, and why drone pilots should familiarize themselves with this valuable resource.
The Need for METAR Reports:
Weather conditions have a significant impact on aviation safety. Pilots must have access to up-to-date and detailed weather information to make informed decisions before takeoff, during flights, and when planning landings. METAR reports provide vital data such as temperature, wind speed and direction, visibility, cloud cover, precipitation, and atmospheric pressure. This information allows pilots to assess the current weather situation and adjust their flight plans accordingly, ensuring the safety of the aircraft and its occupants.
Format of METAR Reports:
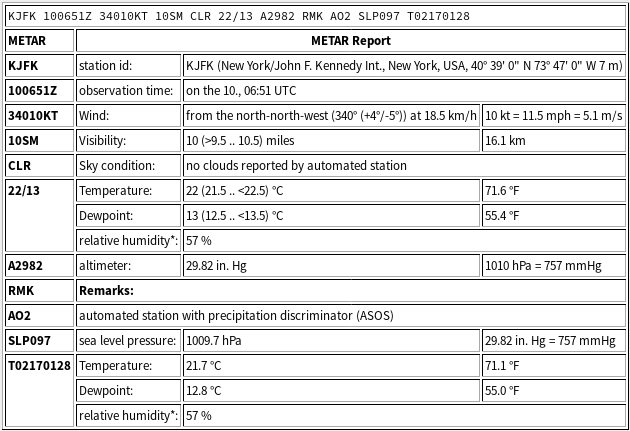
METAR reports follow a standardized format to ensure consistency and ease of interpretation. Each report consists of coded elements that convey specific weather parameters. Here is an example of a METAR report:
METAR EHAM 281200Z 04010KT 9999 FEW022 SCT040 16/10 Q1015 NOSIG
Breaking down the example:
- EHAM: The ICAO code for the airport or aerodrome from which the report originates.
- 281200Z: The date and time of the observation in UTC (Coordinated Universal Time).
- 04010KT: Wind direction and speed (040 degrees at 10 knots).
- 9999: Visibility in meters (9999 indicates visibility is greater than 10 kilometers).
- FEW022 SCT040: Cloud cover (few clouds at 2,200 feet, scattered clouds at 4,000 feet).
- 16/10: Temperature and dew point (16 degrees Celsius and 10 degrees Celsius, respectively).
- Q1015: Atmospheric pressure (1015 hPa).
- NOSIG: No significant changes expected in the weather conditions.
Who Needs to Know and How to Read METAR Reports:
METAR reports are essential for various aviation stakeholders, including pilots, air traffic controllers, meteorologists, and flight dispatchers. Understanding how to read a METAR report is vital to extract relevant weather information accurately. Here are a few key points to consider:
- Codes and Abbreviations: Familiarize yourself with the commonly used codes and abbreviations in METAR reports. Resources such as aviation weather training materials and online guides can provide comprehensive lists for reference.
- Interpretation of Elements: Each element in a METAR report corresponds to specific weather parameters. By understanding the codes, pilots can interpret information regarding wind speed, visibility, cloud cover, temperature, pressure, and more.
- Time and Validity: Pay attention to the date and time of the observation, usually mentioned at the beginning of the report. METAR reports are typically issued every hour, but it's important to note their validity, as weather conditions can change rapidly.
Importance for Drone Pilots:
Drone pilots share the airspace with manned aircraft, making it crucial for them to have a comprehensive understanding of weather conditions. By familiarizing themselves with METAR reports, drone pilots can assess the suitability of weather conditions for safe drone operations. Factors such as wind speed, visibility, and cloud cover are particularly important for drone flights, as they directly impact flight stability, visual line of sight, and obstacle avoidance capabilities. A thorough understanding of METAR reports enables drone pilots to make informed decisions regarding flight planning, scheduling, and airspace safety.

Exadatum
Exadatum is a leading technology company specializing in data analytics, data science, data engineering, and large-scale systems. With a strong focus on leveraging AI, Robotics and Drones, Exadatum is building next generation products and services.
-

Abhijit Shingate
CEO & Founder
Abhijit's deep passion lies in the realm of innovation. Throughout his career, he has consistently achieved remarkable results, committing himself to harnessing data-driven solutions and state-of-the-art AI technologies to transform the drone and robotics industry.
Do you want to be part of exciting journey of the future of AI, Robotics and Drones?
With the convergence of data, AI, robotics, and drones, we see immense potential for transformative impact across industries. Leveraging our expertise in data analytics, AI, and large-scale systems, we are determined to shape the future of robotics and drones by infusing intelligence and autonomy into these technologies.
© 2023 Exadatum Software Services Private Limited. All rights reserved.